Organ-on-a-chip (OOC) technology is a significantly used emerging technology in cell biology and...
Pipettes are essential tools in any laboratory, and proper care can significantly extend their...
The principle of RT-PCR (Reverse Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction) involves two main steps:...
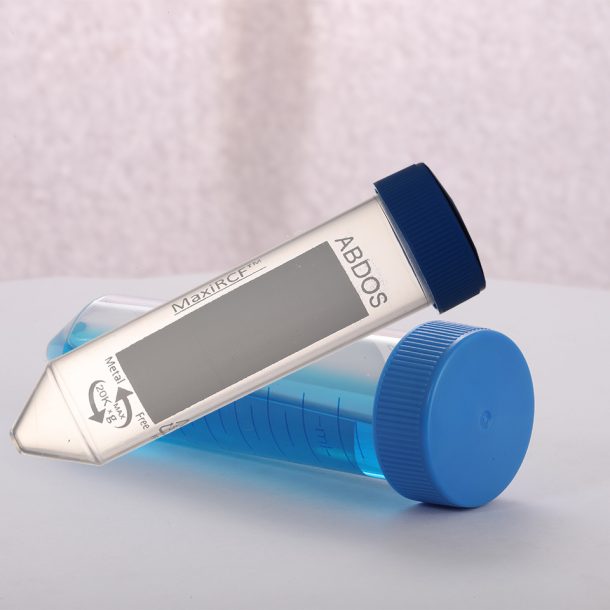
Centrifuge tubes have played a crucial role in laboratory practices, particularly in the separation...
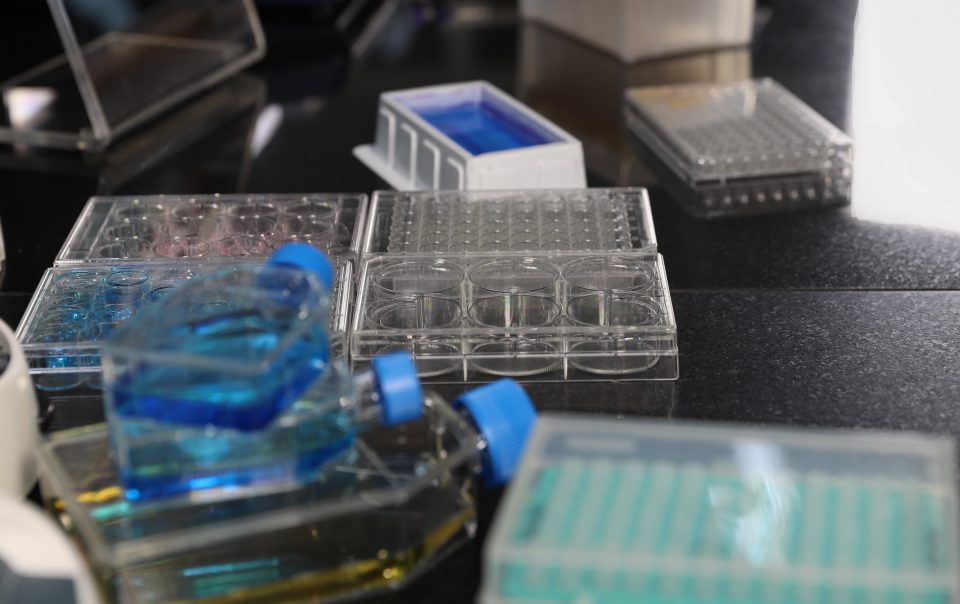
For many years, cell culture has been essential to drug development, biological research, and...
Pipette Tip Box Design – A crucial factor in preventing pipetting errors Dispensing the exact...